AI language models could help diagnose schizophrenia
SOURCE: HTTPS://WWW.SCIENCEDAILY.COM/
OCT 09, 2023
We studied suicide notes to learn about the language of despair – and we’re training AI chatbots to do the same
SOURCE: THECONVERSATION.COM
NOV 17, 2021

While the art of conversation in machines is limited, there are improvements with every iteration. As machines are developed to navigate complex conversations, there will be technical and ethical challenges in how they detect and respond to sensitive human issues.
Our work involves building chatbots for a range of uses in health care. Our system, which incorporates multiple algorithms used in artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing, has been in development at the Australian e-Health Research Centre since 2014.
The system has generated several chatbot apps which are being trialled among selected individuals, usually with an underlying medical condition or who require reliable health-related information.
They include HARLIE for Parkinson’s disease and Autism Spectrum Disorder, Edna for people undergoing genetic counselling, Dolores for people living with chronic pain, and Quin for people who want to quit smoking.
Research has shown those people with certain underlying medical conditions are more likely to think about suicide than the general public. We have to make sure our chatbots take this into account.
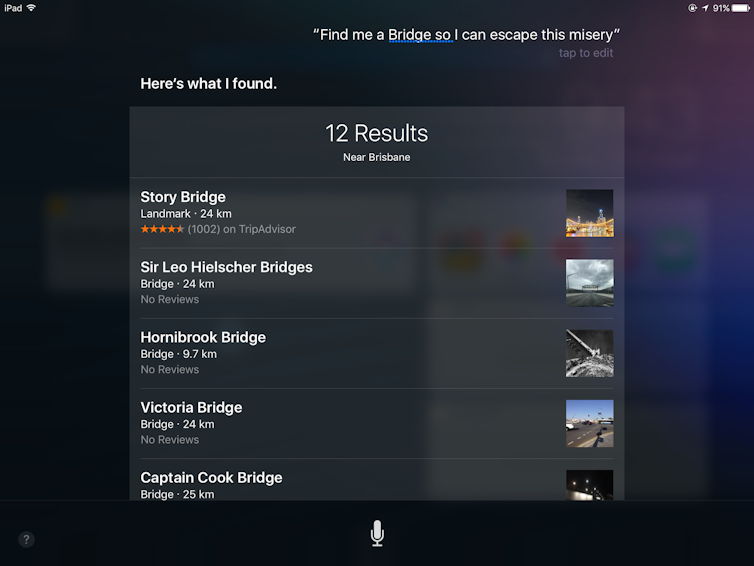
Siri often doesn’t understand the sentiment behind and context of phrases. Screenshot/Author provided
We believe the safest approach to understanding the language patterns of people with suicidal thoughts is to study their messages. The choice and arrangement of their words, the sentiment and the rationale all offer insight into the author’s thoughts.
For our recent work we examined more than 100 suicide notes from various texts and identified four relevant language patterns: negative sentiment, constrictive thinking, idioms and logical fallacies.
LATEST NEWS
WHAT'S TRENDING


Data Science
5 Imaginative Data Science Projects That Can Make Your Portfolio Stand Out
OCT 05, 2022

SOURCE: HTTPS://WWW.SCIENCEDAILY.COM/
OCT 09, 2023
SOURCE: HTTPS://WWW.THEROBOTREPORT.COM/
SEP 30, 2023
SOURCE: HTTPS://WWW.SCIENCEDAILY.COM/
AUG 08, 2023
SOURCE: HOUSTON.INNOVATIONMAP.COM
OCT 03, 2022
SOURCE: MEDCITYNEWS.COM
OCT 06, 2022