Digital twins on the manufacturing menu – with help from the hyperscalers
SOURCE: HTTPS://WWW.IOTTECHNEWS.COM/
NOV 16, 2023
Tata Consultancy Services offers smart factory implementation roadmap
SOURCE: ARCWEB.COM
SEP 26, 2021

Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) recently presented to ARC their strategy and offering for implementing the Smart Factory. In keeping with the overall theme and context of digital transformation, TCS proposes a comprehensive innovation-led approach within a manufacturing setup. In the business context, TCS delivers a set of solutions to customers that will enable them to transform their traditional factories into digital factories.
The Smart Factory, a TCS Neural Manufacturing solution, is one of several “Big Bet” themes that TCS is offering to their customers, which also includes Resilient Supply Chain, Connected Workforce, and Connected Products. TCS is targeting key KPI improvement areas, such as productivity, sustainability, agility, speed-to-market, and customization where transformation to smart manufacturing will provide real and tangible benefits and opportunities to gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. While a few companies have attained levels of maturity in making the transition to a digital factory, most are incrementally experimenting at a smaller scale, but steadily moving towards higher maturity levels and the state of the “Smart Factory.”
TCS maintains that several KPI areas can achieve significant quantitative improvements through the implementation of a Smart Factory initiative, specifically in the area of productivity. These include OEE improvement, quality cost reduction, inventory reduction, speed-to-market time reduction, operating cost reduction, and energy efficiency. Each of these areas represent candidates for process improvement that the technology and methodology of a Smart Factory can directly address. The TCS Smart Factory offering provides manufacturers with a roadmap of capabilities that will enable them to progress through the Smart Factory maturity stages - from traditional factories to connected and smart, to self-aware, and finally to autonomous factories.
In the context of today’s manufacturing environment where the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Manufacturing 4.0 have mandated that factories must be intelligent and connected, the definition of a Smart Factory would have to include these elements and more. In essence, a Smart Factory is a highly digitized production facility that relies on fully integrated, collaborative manufacturing systems that are able to respond in real-time to changing and dynamic conditions. A Smart Factory also relies on advanced information and manufacturing technologies that allows for the access of real-time operational information that drive advanced analytics. Implementation of a digital twin is often an integral component of a Smart Factory system.
Having a factory that uses smart, connected production equipment and devices allows for data-driven decision-making that enables efficiency and productivity throughput. By introducing the use of advanced analytics powered by AI/ML allows the factory systems maturity levels to progress from connected and intelligent to self-awareness, and ultimately to autonomous systems.
There are four levels that can be used to assess the journey through the improvement process to becoming a smart manufacturer. The levels begin with factories that have data/information that is available but not readily accessible. The next level would be manufacturers with more accessible and structured data in more usable forms. Progressing to AI/ML powered real-time operational data that enables predictive analytics would be the next stage. Finally, action-oriented data is used to create prescriptive solutions that improve the process and determine best practices.
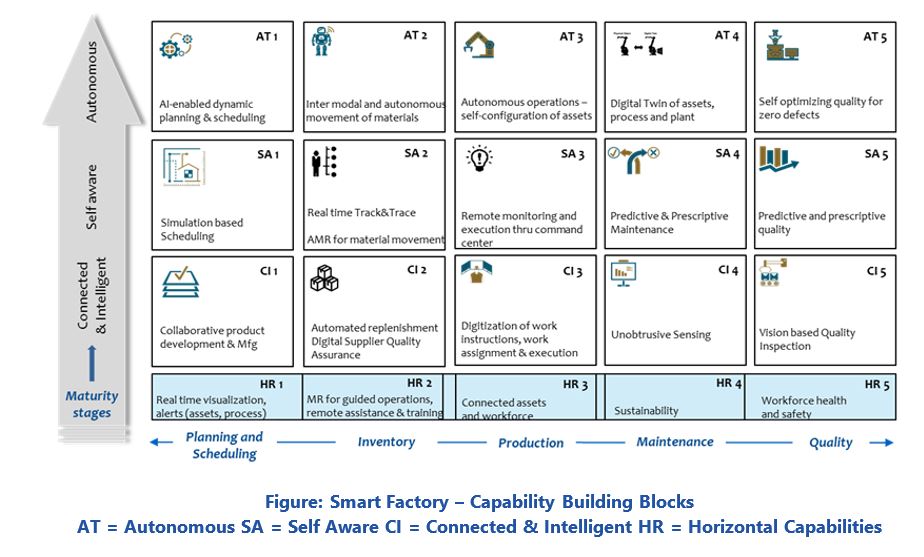
TCS has created a Smart Factory Construct based on Neural Manufacturing, a thought leadership framework that enables an organization and its ecosystems to become connected, cognitive, and collaborative. Neural Manufacturing envisions the traits of intelligent, connected, automated, adaptive, personalized, cognitive, and resilient factory systems. The construct is fundamentally based on progression through the three maturity stages of smart manufacturing systems -- connected and intelligent, self-aware, and autonomous. It provides specific attributes at each maturity level for operational characteristics, capability building blocks, use cases, and fundamental capabilities.
For example, at the connected and intelligent maturity level, operational characteristics would include interconnected production systems, real-time visibility, and intelligent edge devices. Moving to the self-awareness maturity level, operational characteristics include AI/ML driven self-aware systems, human/machine coexistence, and a connected ecosystem. With autonomous operations, it would become completely data-driven, with autonomous and adaptive changeovers and improvements. This enables a design, manufacture, and operate anywhere environment. Autonomous operations leverage AI/ML for planning and scheduling, quality assurance, and operational digital twins.
The TCS Smart Factory offering currently contains 20 specific capabilities over the three maturity stages. These capabilities apply to areas such as planning and scheduling, inventory, production, maintenance, and quality. Examples of these capabilities include digitalization of work instructions, vision-based quality, predictive/prescriptive maintenance, AI enabled planning and scheduling, digital twin of assets and factory, and self-optimizing quality assurance. In addition to capabilities the Smart Factory offering includes over 70 use cases.
To help customers in the implementation process, TCS uses a Smart Factory Sandbox approach for value discovery. Customers are able to utilize real-time shop floor data to experiment and refine results with shop floor variations. This way users are able to identify high impact use cases across their manufacturing value chain and prepare components for a rapid build and execution.
TCS offers a roadmap for Smart Factory implementation in the context of increasing business value as a manufacturer progresses through the maturity stages. The concept is to plan big, lay a foundation based on discovery, start with a small pilot project, and implement a rapid build based on proof-of-concept (POC).
Manufacturers can transform to future enterprises with TCS Smart factory solution based on the tenets of IIoT and Manufacturing 4.0. To establish a Smart Factory, there must be adherence to key principles that define this intelligent, connected, self-aware, and autonomous ecosystem. TCS’ Smart Factory roadmap provides a way for manufacturers to implement a smart factory within a maturity progression and business value context. This approach enables companies to move towards flexible manufacturing and an end-to-end connected ecosystem player. Using AI/ML for predictive/prescriptive maintenance and quality and implementing digital twins of product, process, and assets enables a pathway to autonomous factories.
LATEST NEWS
WHAT'S TRENDING


Data Science
5 Imaginative Data Science Projects That Can Make Your Portfolio Stand Out
OCT 05, 2022

SOURCE: HTTPS://WWW.IOTTECHNEWS.COM/
NOV 16, 2023
SOURCE: HTTPS://AITHORITY.COM/
OCT 03, 2023
SOURCE: HTTPS://WWW.SCIENCEDAILY.COM/
AUG 08, 2023
SOURCE: HTTPS://WWW.GLOBALLOGIC.COM
JUL 06, 2023
SOURCE: HTTPS://INDIAAI.GOV.IN/ARTICLE/HOW-DIGITAL-TWIN-TECHNOLOGY-WILL-EVOLVE-IN-2023
JUL 04, 2023
SOURCE: HTTPS://WWW.CNBC.COM/2023/01/21/DIGITAL-TWINS-ARE-SET-FOR-RAPID-ADOPTION-IN-2023.HTML
JUN 30, 2023